Global Energy Storage Batteries Enter the “Popularization Phase”
Energy storage batteries are a necessary condition for promoting renewable energy. Currently, energy storage batteries have entered a widespread “popularization phase.” In 2023, global new energy storage battery capacity will reach 30 gigawatts, an 87% increase from the previous year, with a tenfold growth in size within five years. The price of lithium batteries has also dropped by 60% in five years. The energy storage battery industry has also received significant subsidies from governments around the world. However, achieving the goal of reducing greenhouse gas emissions close to zero remains difficult, necessitating urgent improvements in energy storage battery supply capacity.
Energy storage batteries are key to making renewable energy a primary source of electricity. The output of solar and wind energy depends on the weather. To effectively utilize these energy sources, it is necessary to establish a system to store electricity in batteries during appropriate times and use the stored power during adverse weather conditions.
Currently, the energy storage battery market is dominated by China. China is promoting the development of renewable energy nationwide. In 2022, China installed 5.6 gigawatts of new energy storage batteries, 2.3 times that of 2021, accounting for 34% of the global total and ranking first in the world.
Europe, which accounts for 27% of the global share, is also constructing large-scale energy storage plants. Spanish utility giant Iberdrola invested 28 million euros in 2022 to build a 0.05-gigawatt large-scale energy storage plant in Ireland, which has already been put into operation.


On the other hand, Japan’s share in the global energy storage battery market is only 2%. Japan has been slow in commercializing energy storage batteries. Japan implements a fixed pricing system for electricity, so the demand for battery storage of electricity has not significantly increased.
By 2030, the projected global new battery storage capacity is expected to reach 87 gigawatts, nearly three times that of 2023. It is estimated that the energy storage battery industry will expand at an average annual rate of 23% from now until 2030. This means that energy storage batteries have finally entered a period of widespread use.

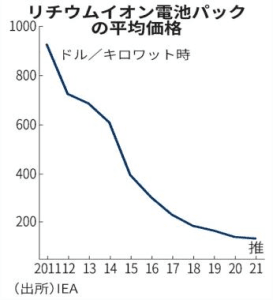
Behind this is the fact that the manufacturing cost of energy storage batteries has significantly declined, which was once the biggest constraint on their development. According to data from the International Energy Agency, the price of lithium-ion battery packs has dropped by 60% in five years, reaching $132 per kilowatt-hour in 2021. In addition, significant government subsidies have played a role.
On April 20th, the US Department of Energy announced that it would provide up to $3 billion in loan guarantees for the installation of rooftop solar power systems and batteries, encouraging people to install solar panels and energy storage batteries at home and attempt collective control and operation of distributed power. This is a technology known as a Virtual Power Plant (VPP), which utilizes energy storage batteries to adjust fluctuating power demand due to time and location, making power usage more efficient. In some areas, energy storage batteries have become a critical factor in maintaining power stability.
Source: “Nikkei Economic News”
